To study the common food adulterants in honey, turmeric powder, Chilli powder and pepper
Objective / Aim of the Experiment
To measure the value of high resistance by substitution method
Apparatus Required
Given high resistance
DC Power Supply
Galvanometer
High resistance boxes
One way key
Two way key
Connecting wires
Formula Used
X = [{R (G+S)/S}+G]θ2/θ1 - G
Where, G = Resistance of galvenometer
S = resistance of Shunt
R= high resistance
θ1, θ2 = Diflection with X and R, S
Circuit Diagram for Substitution Method
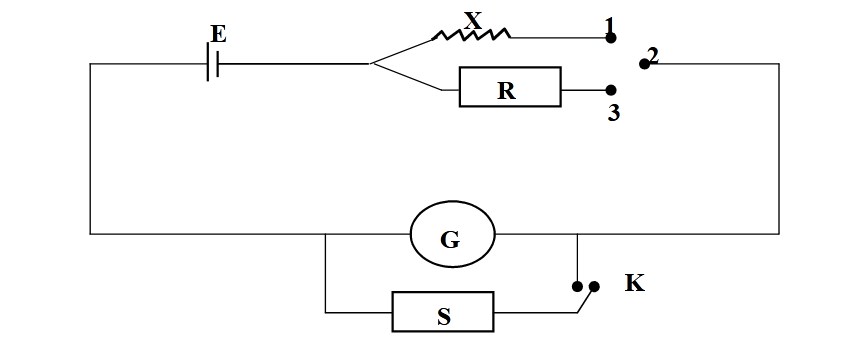
Theory
The connections are made as shown in Fig. below.The key between the terminals 1 and 2 is inserted so as to pass current through the unknown resistance X and the deflection of the galvanometer is noted. The current passing through the galvanometer, Ig, is given by
Ig = E / (R+G) .............. (1)
Here E is the e.m.f. of the battery and G is the galvanometer resistance. The key between 1 & 2 are now removed. Some high resistance, R, from the resistance box is introduced and key between the terminals 3 and 2 is inserted. As R >> X, the galvanometer will give larger deflection which may be out of range. Insert the key K and adjust the value of shunt resistance, S, so that deflection in galvanometer is same as it was with X earlier. The current passing through the galvanometer, Ig, is given by
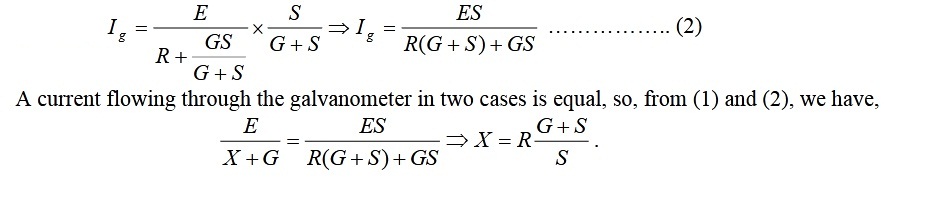
Procedure
Make the connections as shown in earlier figure.
(a) Introduce high resistance from R and then inert plug between 1 & 2 of two way key. Adjust R to get full deflection in the galvanometer. Note this deflection n and value of R.
(b) Insert plug in key K. Keeping R fixed adjust S so that the deflection in the galvanometer becomes half of the previous deflection, i.e., n/2. Note this deflection and the value of S.
(c) Repeat steps (2) & (3) for different R.
(d) Remove plug from 2 & 3, and, insert into terminal between 1 & 2 to bring the unknown resistance X in the circuit. Remove plug in key K. Note down the deflection.
(e) Remove plug from 1 & 2, and, insert into terminal between 2 & 3. Insert plug in key K. Take out a resistance from high resistance box R. Adjust the value of S so that the deflection is exactly the same as in the previous step.
(f) Repeat step (e) for different combinations of R & S.
Observation Table
The value of G = 02 K Ω

Result
The value of X is ...............................K Ω
Precautions
- A high resistance sensitive galvanometer should be used.
- Plugs of resistance boxes, keys should be tight.
Viva Questions and Answers
Question-1: What is galvanometer?
Answer-1: A device used to detect the presence of current in a circuit.
Question-2: How will you find resistance of a galvanometer?
Answer-2: Resistance of a galvanometer can be found by tw0 methods: Equal deflection method and Half deflection method.
Question-3: Explain substitution method?
Answer-3: In this method current is first passed through resistanceand deflectiion in the galvanometer is noted after this unknown resistance is replaced by resistance R and shunt S, the values of R and S are adjusted in such a manner that galvanometer shows same deflection. The value of unknown resistance is given as: X = R(G+S)/S
Question-4: What is the deflection between galvanometer and ammeter?
Answer-4: The resistance of ammeter is higher than that of galvanometer. Further, galvanometer is used to detect the presence of current in the circuit whereas ammeter is used to measure low current in the circuit.
Question-5: What is shunt?
Answer-5: A shunt is a small resistance connected in parallel with galvanometer. It provides a bypass of current through the galvanometer.
Tags:
Image Credits: Freepik








