To study the common food adulterants in honey, turmeric powder, Chilli powder and pepper
Light is one of nature's most captivating phenomena, bending, bouncing, and transforming in ways that have puzzled scientists and amazed observers for centuries. Understanding the difference between reflection and refraction isn't just academic—it's the key to unlocking the secrets behind everything from why the sky appears blue to how fiber optic cables carry our internet data.
What Is Reflection of Light? ⚡
Reflection occurs when light waves bounce off a surface and return to the medium from which they came. Think of it like a ball bouncing off a wall—the light hits a surface and rebounds at the same angle.
Key Characteristics of Reflection:
- Light stays in the same medium
- Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection
- No change in speed or wavelength
- Creates mirror images and shiny surfaces
Fun Fact:
The word "reflection" comes from Latin "reflectere," meaning "to bend back"—exactly what light does!
What Is Refraction of Light? ????
Refraction happens when light passes from one medium to another (like air to water) and changes direction due to a change in speed. This bending of light is responsible for some of the most beautiful optical illusions in nature.
Key Characteristics of Refraction:
- Light enters a different medium
- Light changes speed and direction
- Wavelength may change
- Creates bending effects and optical illusions
Amazing Fact:
A pencil partially submerged in water appears bent because light refracts as it moves from water to air!
Side-by-Side Comparison: Reflection vs. Refraction
| Aspect | Reflection | Refraction |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Change | No - stays same | Yes - enters new medium |
| Light Path | Bounces back | Bends/changes direction |
| Speed | Remains constant | Changes speed |
| Angle Relationship | Angle of incidence = angle of reflection | Follows Snell's Law |
| Wave Properties | Frequency and wavelength unchanged | Wavelength may change |
| Common Examples | Mirrors, shiny metals | Lenses, prisms, water surfaces |
Real-World Applications That Surround Us Daily
Reflection in Action:
- Mirrors in bathrooms and cars
- Security mirrors in stores
- Periscopes in submarines
- Solar cookers that concentrate sunlight
- Fiber optic cables that bounce light signals
Refraction at Work:
- Eyeglasses correcting vision
- Camera lenses focusing images
- Rainbows after storms
- Stars twinkle due to atmospheric refraction
- Swimming pools appearing shallower than they are
Mind-Blowing Facts About Light Behavior
-
Speed Demon: Light travels at 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum—the fastest speed possible in the universe!
-
Bendy Light: When light refracts through a prism, it separates into its component colors because different wavelengths bend at slightly different angles.
-
Perfect Mirror: The smoothest surfaces reflect up to 99.99% of light, while rough surfaces scatter light in multiple directions.
-
Atmospheric Illusion: The sun appears about 2 minutes before it actually rises due to atmospheric refraction bending light around Earth's curvature.
-
Total Internal Reflection: This phenomenon allows fiber optic cables to carry data across continents by bouncing light signals without loss!
The Science Behind the Magic
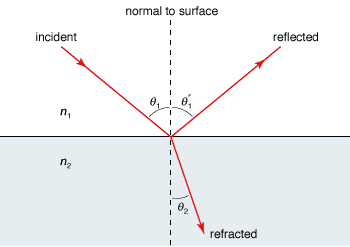
Law of Reflection:
When light hits a smooth surface, it follows a predictable pattern where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Both angles are measured relative to the normal (an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface).
Snell's Law of Refraction:
This mathematical relationship describes how light bends: n₁sin(θ₁) = n₂sin(θ₂) Where n represents the refractive index of each medium and θ represents the angles.
Why Understanding This Difference Matters
Knowing the difference between reflection and refraction helps explain countless everyday phenomena:
- Why does a straw look broken in a glass of water? Refraction!
- How do telescopes and microscopes work? Both reflection and refraction!
- Why do diamonds sparkle so brilliantly? Total internal reflection!
- How do corrective lenses work? Refraction!
Practical Tips for Observation
- Create your own experiments: Use a flashlight, mirror, and glass of water to observe both phenomena
- Watch for refraction: Look at objects partially submerged in water
- Notice reflection: Observe how different surfaces reflect light differently
- Spot the rainbow: Refraction separates white light into colors
The Bigger Picture: Technology and Innovation
Modern technology heavily relies on manipulating light through reflection and refraction:
- Smartphone cameras use multiple lenses (refraction) and mirrors (reflection)
- Telescopes employ both principles to gather and focus light from distant stars
- Lasers utilize carefully controlled reflection for precision applications
- Fiber optic networks depend on total internal reflection for high-speed data transmission
Conclusion: Light's Dual Nature
Understanding the difference between reflection and refraction reveals the elegant simplicity underlying complex optical phenomena. While reflection bounces light back like a mirror, refraction bends light as it travels between different materials. Both processes work together to create the visual world we experience daily.
From the simple mirror in your bathroom to the sophisticated lenses in your camera, these fundamental principles of physics shape how we see and interact with light. Next time you look at a rainbow, watch your reflection in a window, or simply observe how light behaves around you, you'll have a deeper appreciation for these fascinating optical phenomena.
Whether you're a student tackling physics homework or simply curious about the world around you, grasping the basics of reflection versus refraction opens doors to understanding everything from basic eye function to cutting-edge telecommunications technology.
Ready to explore more optical wonders? The next time you're near water, glass, or any reflective or transparent surface, test your knowledge by identifying whether you're observing reflection or refraction in action!
Tags:
Difference between Refraction of Light vs Reflection
Reflection vs Refraction of Light
Differences between Refraction of Light vs Reflection
Image Credits: Freepik








